Insights on Cell Therapy From IO360
- Christina Contreras
- Jul 27, 2022
- 4 min read

Executive Summary
IO360 underscored the importance of the starting cell type, as the overall consensus of the superior cell type was the potent and specific T cell vs. the better controlled / safer option of the NK cell; presentations also emphasized the advantages the naïve T cell phenotype (Tnaive) / stem memory T cells (Tscm) confer in in vivo proliferation, potency, and persistence
Current cell therapy hurdles are centered around exerting therapeutic efficacy in the solid tumor setting, minimizing associated toxicities, and resolving operational obstacles such as manufacturing complexity
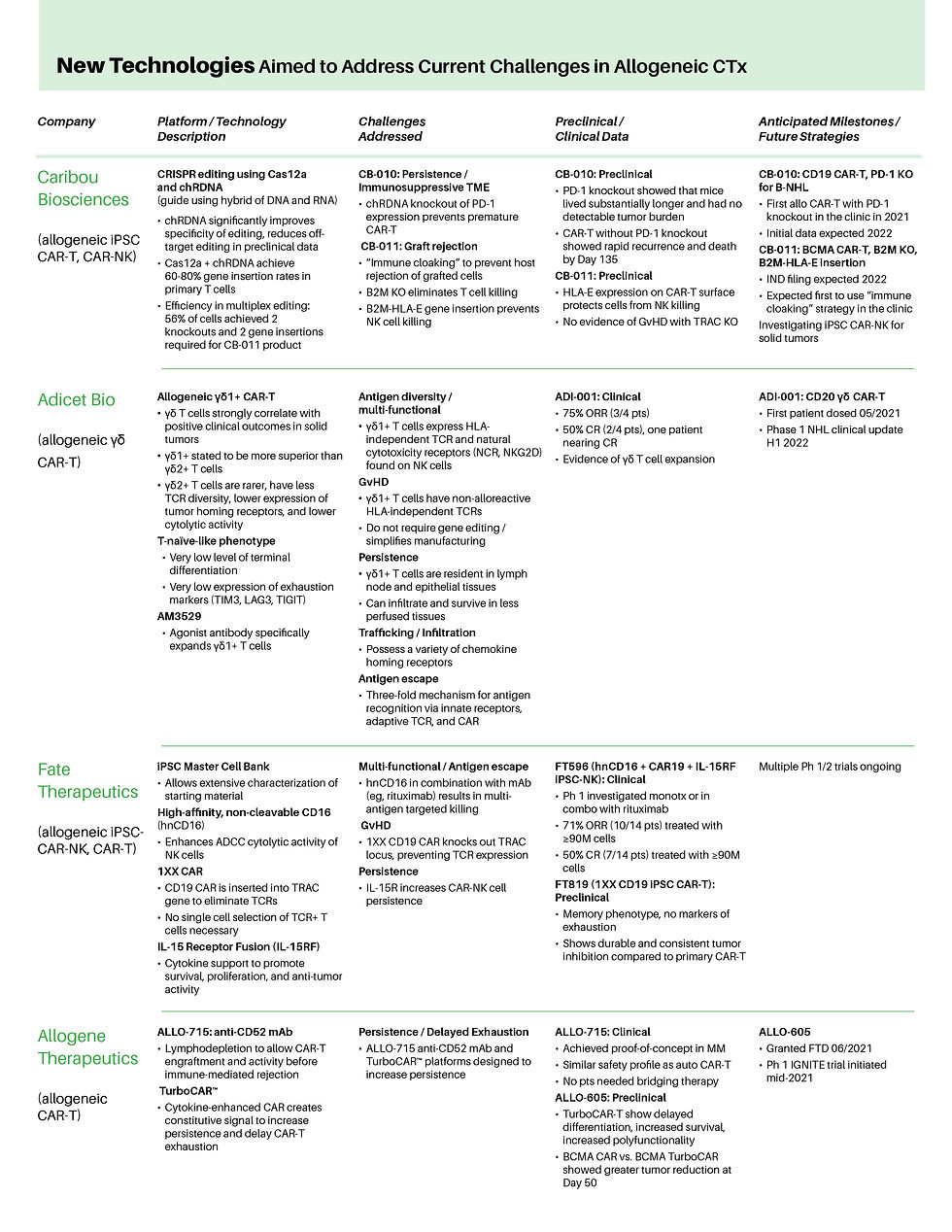
Genome engineering technologies remain a critical component in ensuring a consistent and well-characterized cell therapy product with minimal off-target / off-tumor toxicities
Innovations to address remaining hurdles include “armoring” cells with enhanced cytokine support for enhanced persistence and functionality, knocking out expression of alloreactive components, and circumventing T cell exhaustion in the TME (e.g., via PD-1 knockout)
Preliminary clinical data are beginning to demonstrate proof-of-concept for strategies such as cytokine armoring, and use of specific T cell subtypes such as γδ T cells and naïve T cells have demonstrated improved clinical outcomes
Manufacturing innovations to address operational obstacles focused on reducing ex vivo culture time, using nonviral gene delivery methods, and engineering in vivo CAR-T
Key Theme: Cell Type Matters
T cells emerged as the marginally superior cell type in the black and white debate on T vs. NK cell superiority, as most patients were cited to prefer a robust and complete response with short-term toxicities (T cells) than a less efficacious therapy with a better safety profile (NK cells)

The naïve T cell phenotype was highlighted across multiple programs to exhibit reduced T cell exhaustion, greater in vivo proliferation, and correlation with positive clinical outcomes
Novartis’ T-Charge™ platform is cited to maintain naïve features of T cells for greater potency
BMS’ NEX T platform aims to preserve T cell stemness for CAR-T products, for greater expansion potential, more potent product, and increased manufacturing efficiency
Patients with better clinical response to CAR-T therapy showed a shift toward stem memory T cells (Tscm) and T-naïve phenotype in CD4 and CD8 T cells
iPSCs have strong potential in the allogeneic setting, as stated in multiple presentations
Remaining Challenges in Cell Therapy
Hurdles to achieving efficacy in the solid tumor setting include efficient cell trafficking, infiltration, persistence, and T cell exhaustion in the immunosuppressive TME
Safety concerns need to be managed
Auto: potential for high-grade toxicities (CRS, ICANS)
Allo: requirement for genome editing to avoid GvHD, and alloreactivity depletes the cell therapy graft
Logistical challenges due to long vein to vein times, variability in cell product, high costs due to manufacturing complexity, etc.
Defining the agents and duration of lymphodepletion
Learnings and Developments in Autologous Cell Therapies
[BMS]
Autologous CTx Clinical Learnings
BCMA antigen loss is not a major mechanism of disease progression, as only 4% (3/71 pts) experienced this after ide-cel treatment
5% of CAR-T cells infiltrate the tumor, creating inflammation, resulting in higher response to liso-cel
Future Directions:
The NEX T platform develops cell therapy candidates that have a less differentiated CD8 T cell phenotype, for greater expansion potential, more potent product, and increased manufacturing efficiency
BMS has a strategic collaboration with Century for iPSC-derived CAR for MM and AML
GPRC5D is a novel target in MM and shows expression independent of BCMA
BMS is currently actively enrolling patients in a multi-center trial in the US for GPR5CD-targeted cell therapy
[Novartis]
T-Charge™ Preliminary Clinical Results
Autologous CD19 CAR-T (YTB323) and BCMA CAR-T (PHE885) in Phase 1 trials were developed through the T-Charge™ platform
YTB323 (CD19 CAR-T)
Shown to have promising efficacy of 63% CR across all dose levels, and 73% CR at Dose Level 2 of 12.5M cells
YTB323 showed robust in vivo expansion at a 25-fold lower dose, comparable to the higher end of Kymriah expansion in DLBCL pts
PHE885 (BCMA CAR-T)
53% (8/15 pts) ORR at 3.5 months median follow-up
PHE885 exerted a deep level of response as 34% (2/6 pts) were MRD-negative at 3 months follow-up
T-Cell Based Therapy Insights
[Lumicks] T Cell Binding Avidity vs. Binding Affinity
Binding avidity is defined as the overall strength of interactions between the diversity of receptor-ligand pairs at the cell surface
Optimizing binding avidity is crucial to developing CAR/TCR-T therapies that are effective in tumors with low antigen density
Cellular avidity correlates with in vivo persistence as shown in KRAS G12D-specific TCRs
Mice studies showed CAR-T cells with highest avidity correlated with doubled survival
Intermediate avidity was shown to have minimized on-target, off-tumor toxicity
Binding affinity is defined as the strength of an interaction between a ligand and receptor
Binding affinity has lower impact on T cell function
Correlation of binding affinity with T cell function is a bell-shaped curve; after a threshold affinity, there is decreasing effect on T cell function
[Adaptive] Antigen-Specific TCR Identification
The multiplexed assay for identification of T cell receptor antigen specificity (MIRA) platform is more sensitive at detecting TCR clonotypes than the ELISPOT assay
Peptide-based MIRA uses peptide antigen pools (which can be derived from patient samples) to stimulate PBMCs; T cells activated by specific peptide pools are then sequenced
Transgene-based MIRA identifies neoantigen-specific TCRs that recognize endogenously processed antigens
Targeting neoantigens was highlighted as a promising strategy to develop TCR-T cell based therapies
Innovations In Cell Therapy Manufacturing
Reducing ex vivo culture duration improves the anti-leukemic activity of CAR-T
Ex: Rapid manufacturing of non-activated CD19 CAR-T through a 1-day expansion process was able to induce potent and durable remission of ALL at low doses
Lipid nanoparticle (LNP) / non-viral cargo delivery is a potential option to edit CAR-T cells
Ex: Intellia’s NTLA-5001 uses ex vivo gene editing by LNPs, requiring no electroporation
Ex: Precigen’s PRGN-3006 and PRGN-3007 use non-viral gene delivery via electroporation to co-express ROR1 CAR, membrane-bound IL15, and kill switch overnight
Engineering in vivo CAR-T can be explored to reduce vein to vein time
Ex: Sana is developing in vivo CARs in macaques, using CD8 or CD8-targeted fusosomes with CD20 CAR
T cell quality can be improved by BET bromodomain inhibition, which can restore function of exhausted T cells, as seen in CLL patients
Redundancy is key in manufacturing; smaller facilities with fewer staff and less equipment are more susceptible to errors
For Details on Axiom’s Capabilities, Contact:
Hafiz Sikder – hs@axiomhcs.com

Yorumlar